
4.1: Membrane Structure and Composition Since most cells live in an aqueous environment and the contents of the cell are also mostly aqueous, it stands to reason that a membrane that separates one side from the other must be hydrophobic to form an effective barrier against accidental leakage of materials or water. Regulating binding site properties a.Ěllosteric modulation reversible binding at another (“allo-”) site can be activation or inhibition at 50% binding Saturation: there is a finite number of binding sites Competition: structurally similar molecules can compete for binding and remember: the protein can be an enzyme, receptor, transporter, etc. Protein-ligand binding properties Specificity: binding depends on ligand size, shape, charge Affinity: strength of binding: i.e. at 50% binding fig 3-31Īffinity (different ligands) strength of binding: i.e. at 50% binding fig 3-30Īffinity (different proteins) strength of binding: i.e. at 50% binding fig 3-29Īffinity & saturation strength of binding: i.e. Specificity protein Y specificity greater than protein X specificity fig 3-28Īffinity strength of binding: i.e. Specificity binding depends on ligand size, shape, charge fig 3-27 fig 3-26 at 50% binding Saturation: there is a finite number of binding sites Competition: structurally similar molecules can compete for binding Protein ligand interaction Proteins could be: Ligands would be: enzymes substrates, allosteric regulators receptors chemical messengers transporters transported substances transcription factors transcription regulators any of above drugs 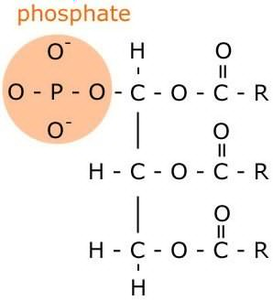
Gap junctions cell-cell communication, small molecules (<1000 MWt) cardiac intercalated disks, smooth muscle fig 3-10d

kidney, gut) paracellular pathway between cells fig 3-10b Tight junctions cell “collar”, block large molecules, no lateral protein movement epithelial tissue (esp.

Intercellular structures Desmosomes “spot welds”, dense proteins (cytoplasm & intercellular) fibers (intermediate filaments) extend across cells epithelial cells (especially skin), cardiac intercalated disks Tight junctions cell “collar”, block large molecules, no lateral protein movement epithelial cells Gap junctions cell-cell communication, small molecules (<1000 MWt) cardiac intercalated disks, smooth muscleĭesmosomes “spot welds”, dense proteins (cytoplasm & intercellular) fibers (intermediate filaments) extend across cells epithelial cells (especially skin), cardiac intercalated disks fig 3-10a Phospholipid structure Amphipathic molecule (phosphatidyl choline) hydrophobic part: fatty acids hydrophilic part: phosphate & choline







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
